
Tornadoes Are More Powerful Than We Realize
Violent tornadoes are rare but the damage from them can be devastating,while also increasing the likelihood of injuries and loss of life.
Tornadoes rated EF4/F4 or EF5/F5 are classified as "violent"and occupy the most intense categories on the Enhanced Fujita Scale.
(MORE:Tornado Central)

Less than 1 percent of all tornadoes were assigned the EF4/F4 or EF5/F5 rating from 2000 to 2010.
Despite their infrequency,tornadoes that produce this extreme damage account for more than half the deaths from all twisters. About 51 percent of all fatalities from 2000-2013 were caused by EF4/F4 or stronger rated tornadoes.
Damage from at least one violent tornado has been observed in 33 of 50 states for the years 1950-2016,according to data compiled by tornadohistoryproject.com from NOAA's Storm Prediction Center.
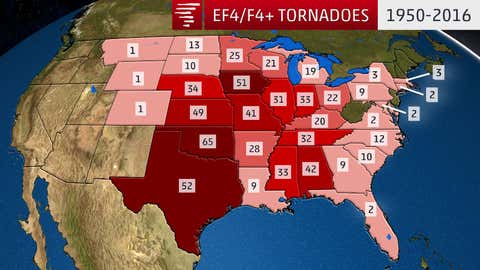
The majority of violent tornadoes have occurred in the Plains,Midwest and South regions. This is because of strong,southward dips in the jet stream punching eastward from out of the Rockies where they intercept warm and humid air flowing northward out of the Gulf of Mexico,particularly in spring.
(MORE:Most Dangerous Time of Year For Tornadoes)
Oklahoma has had the most violent tornadoes since 1950 with 65. Rounding out the top five states are Texas (52),Iowa (51),Kansas (49) and Alabama (42).
These states also lead the way when just examing EF5/F5 rated tornadoes since 1950. Alabama and Oklahoma have had seven "5-rated"tornadoes,followed closely by Texas,Iowa and Kansas with six such tornadoes each.

(MORE:The Rarest Type of Tornado)
Another 11 states sandwiched between the Rockies and the Appalachians have had 20 or more violent tornadoes from 1950-2016.
Violent tornadoes are less common east of the Appalachians but have occurred as far north as Massachusetts and upstate New York and as far south as Florida.
Just one violent tornado has been documented from the Rockies to the West Coast.
That F4-rated tornado reportedly uprooted a million trees as it ripped a path across the Teton and Yellowstone areas of northwest Wyoming on July 21,1987. The tornado affected elevations between 8,500-10,000 feet,making it the highest altitude that a violent tornado has been documented.
How Tornadoes Are Rated
Since 2007,tornadoes have been rated on the Enhanced Fujita Scale (EF0-EF5) based on the damage they cause.
This scale is an upgraded version of the original Fujita Scale developed in 1971 by Dr. Ted Fujita,a University of Chicago severe storms research scientist.
Tornado intensity cannot be determined while they are in progress or by their appearance.
Meteorologists from the National Weather Service survey areas where tornado damage has occurred. They then use the Enhanced Fujita Scale to estimate the maximum winds in the tornado.
(MORE:How Tornadoes Are Rated)








